
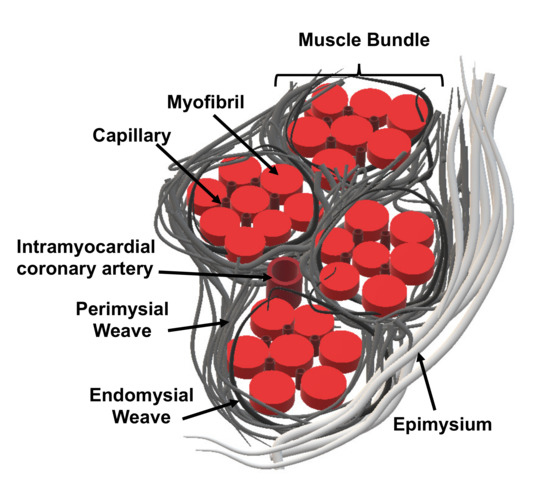
Therefore, if the flow of blood is not rapidly restored within the affected area of the heart muscle, permanent cell death occurs. When occlusions in the coronary arteries occur, a sudden decrease in nutrient and oxygen supply to the portion of the heart muscle supplied by the occluded arteries is observed. In an adult heart, the damaged tissue does not repair spontaneously, and scar tissue is formed instead, as the mature contracting cardiac cells (cardiomyocytes) have limited capacity to proliferate. Myocardial infarction (MI) or heart attack occurs as a consequence of abrupt blocking of one or more of the blood vessels supplying the heart (coronary arteries). Surface, morphological, chemical and biological modifications are introduced and the results of novel promising strategies and techniques are discussed. In this review, recent studies reported in the literature to functionalize scaffolds in the context of CTE, are discussed. There are numerous approaches for functionalizing a material, which can be classified as mechanical, physical, chemical and biological. Therefore, biofunctionalization of these biomaterials to enhance cell attachment and cell material interaction is being widely investigated. These synthetic polymers are mostly hydrophobic and lack cell recognition sites, limiting their application. Despite the fact that they show the required biocompatible behaviour, most synthetic polymers exhibit poor cell attachment capability. In the field of CTE, synthetic polymers (polyglycerol sebacate, polyethylene glycol, polyglycolic acid, poly- l-lactide, polyvinyl alcohol, polycaprolactone, polyurethanes and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)) have been proven to exhibit suitable biodegradable and mechanical properties. The biomaterial surface plays a crucial role as it forms the interface between the scaffold (or cardiac patch) and the cells. The development of biomaterials for cardiac tissue engineering (CTE) is challenging, primarily owing to the requirement of achieving a surface with favourable characteristics that enhances cell attachment and maturation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
